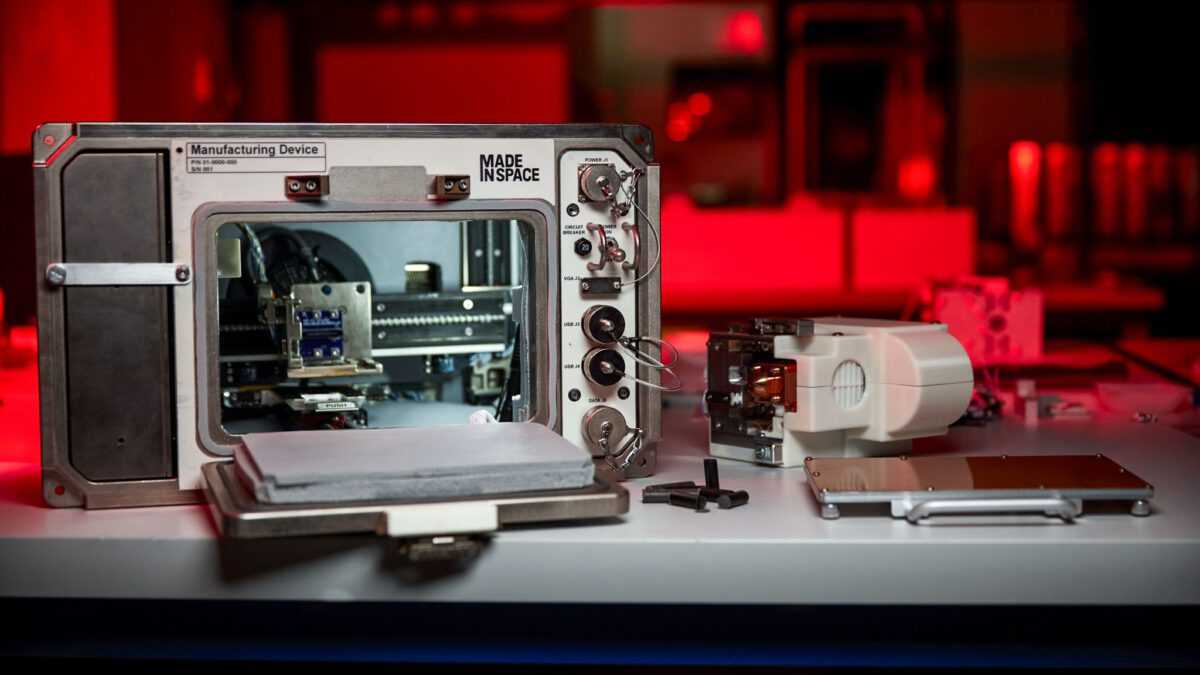
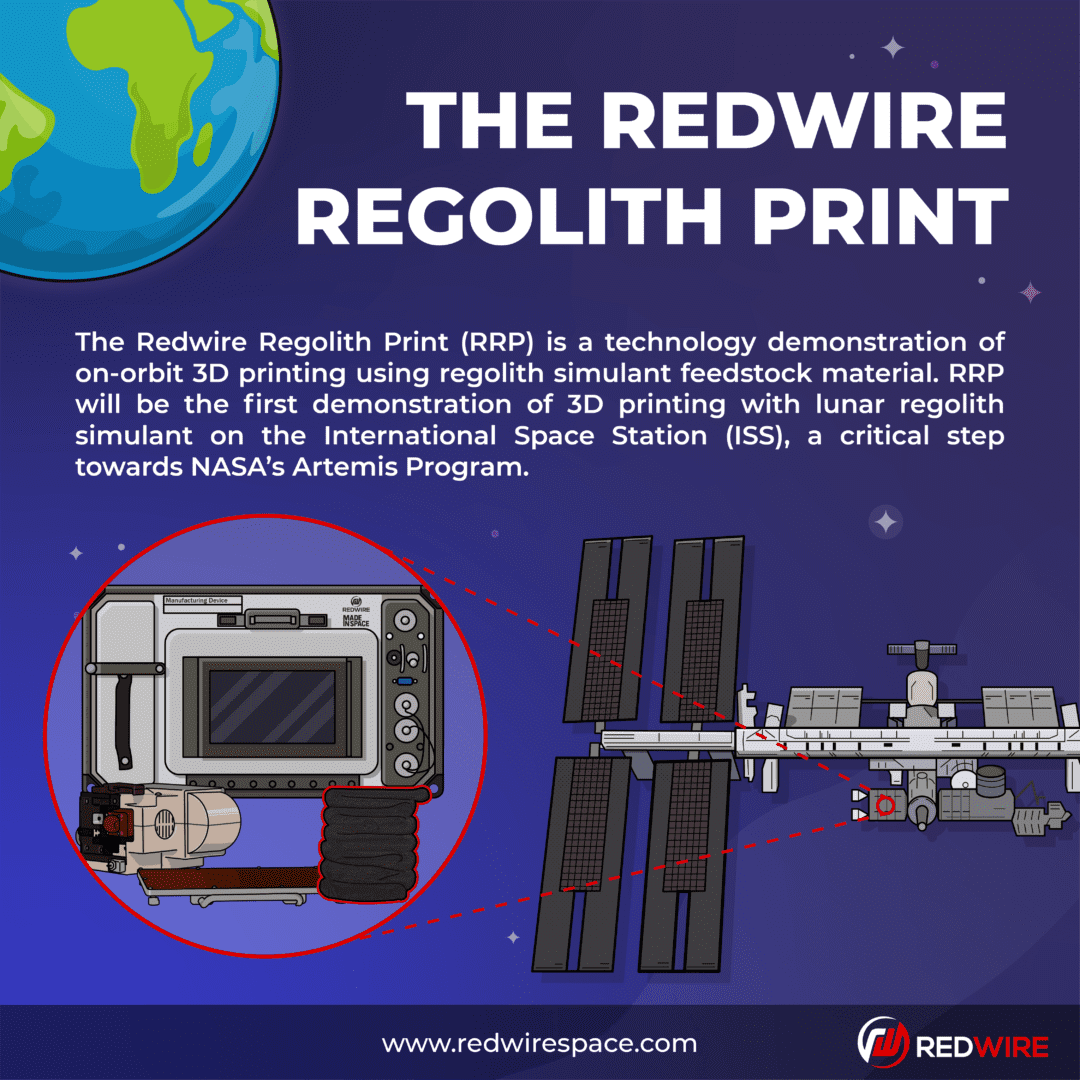
Μέσα στο ‘μεταφορικό’ της NASA, το τελευταίο Northrop Grumman Sygnus resupply διαστημικό όχημα υπάρχει ένας εκτυπωτής. Είναι ένας 3D regolith εκτυπωτής που θα ταξιδέψει στον International Space Station (ISS). Η Διαστημική…
…υπηρεσία μιλά για το Redwire Regolith Print (RRP) project που ουσιαστικά μετατρέπει σκόνη που βρίσκεται στην Σελήνη σε στέρεα αντικείμενα. Το νέο μηχάνημα θα δουλεύψει μαζί με το σημερινό σύστημα εκτύπωσης στον ISS, το ManD, για να δοκιμάσει 3D printing ρεγόλιθου. Τα αποτελέσματα θα μελετηθουν και “could help determine the feasibility of regolith as a raw material and 3D printing as a technique for construction on future space missions,” όπως λέει ο λογαριασμός twitter του ISS Research.
Redwire Regolith Print tests 3D printing using simulated regolith (loose rock and soil found on the surfaces of planetary bodies). Results could help determine the feasibility of regolith as a raw material and 3D printing as a technique for construction on future space missions. pic.twitter.com/MIYq2z5smw
— ISS Research (@ISS_Research) August 10, 2021
Redwire Regolith Print tests 3D printing using simulated regolith (loose rock and soil found on the surfaces of planetary bodies). Results could help determine the feasibility of regolith as a raw material and 3D printing as a technique for construction on future space missions. pic.twitter.com/MIYq2z5smw
— ISS Research (@ISS_Research) August 10, 2021
“The Redwire Regolith Print mission is an important step for proving these advanced manufacturing processes and ultimately accelerating NASA’s exploration timeline to establish a permanent human presence on the Moon,” said Michael Snyder, Chief Technology Officer of Redwire, in a statement.
If the tests succeed, RRP could allow astronauts to print a portion of soil-based habitats on-demand, which could reduce the amount of construction equipment NASA would need to bring to the Moon and Mars on future missions. The space agency has said it plans to look further into the potential for 3D printing habitats on Mars.
Related posts
Categories
- android World
- cinemart / music / video
- comicmania / books
- computing / social media
- consumer electronics
- design / architecture
- ecotech / electric
- exhibitions
- faq / Infographics
- futuristas / iDea
- gadgetfreak taste
- gadgets / stuff
- gaming / fun
- iOS World
- legends / special
- men's world
- military / aviation
- mobile / smartphones
- space talk
- tablets / multimedia
- tech talk / science
- transport / concept